Blog
Top 100+ Systematic Review Topics: A Guide to Finding the Best Systematic Literature Review Topics and Ideas
How to Choose the Best Systematic Review Topics for Your Research
Choosing the best systematic review topic is a critical step in conducting a comprehensive and evidence-based research project. Here are the key steps and insights to guide you in selecting a topic that will not only be impactful but also suitable for your research goals.
Understanding the Importance of Systematic Review in Scientific Research
- Systematic reviews are an essential tool for synthesizing existing research on a specific topic to provide a thorough evaluation of the evidence.
- They help researchers synthesize data across multiple studies, offering a comprehensive summary that informs clinical and scientific practice.
- A well-conducted systematic review is a powerful means to evaluate healthcare interventions, treatments, or policies, offering insight into the effectiveness of various strategies based on evidence-based findings.
- By analyzing existing literature, a systematic review minimizes uncertainty and strengthens the reliability of conclusions drawn from research.
- The review process ensures that the gathered data is rigorous, transparent, and replicable.
Systematic Literature Review Help
Looking to streamline your research? Our systematic literature review writing services offer thorough, high-quality analysis to help you stay ahead. Get in touch with us today to elevate your academic work!
How to Formulate a Research Question for a Systematic Review
- Begin by identifying a gap in the existing literature. This could be a specific intervention or approach that has not been sufficiently explored.
- Frame your research question based on the gaps you’ve identified. A good research question should be clear, focused, and address a specific issue or context in healthcare or another field.
- Consider using frameworks like PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) to specify the parameters of your systematic review question.
- Ensure that your research question can be answered by synthesizing available data through rigorous methods. This helps inform the synthesis process and ensures a comprehensive review.
- Your question should also allow for variations in study designs, as different types of studies (e.g., behavioral, clinical) may be included in your review.
- Think about the preliminary research findings and the need for further publication on the chosen topic. This can guide you in selecting a topic that adds value to the existing body of literature.
Key Criteria for Selecting the Best Systematic Review Topic
- Relevance: Choose a topic that is significant in your field, addressing an important issue or problem that requires evidence synthesis.
- Feasibility: Ensure that sufficient research is available in the chosen area to conduct a meaningful review. Database searches should yield a variety of studies for a robust synthesis.
- Impact: Select a topic that will provide valuable insight into existing practices or policies, ideally contributing to evidence-based changes in the field.
- Specificity: Be specific when choosing a topic. Too broad of a subject will make it difficult to narrow down the focus during the search strategy phase.
- Gap in Literature: There should be a clear gap in current research or a need for more rigorous evidence on a topic that is underexplored.
- Target Audience: Consider who will benefit from your findings. For example, in healthcare, nurses, clinicians, or policymakers might be the primary audience for your systematic review.
Top 15 Systematic Review Topics in Nursing
- Impact of Behavioral Interventions in Diabetes Management: Explore how different interventions affect the management of diabetes in various populations.
- Effectiveness of Telehealth in Post-operative Care: Investigate how telehealth practices contribute to post-surgery recovery, reducing hospital readmissions.
- Nursing Approaches to Pain Management in Cancer Patients: Review evidence on the most effective nursing interventions in managing cancer pain.
- Nutritional Support for Critically Ill Patients: Assess how nutritional interventions impact recovery in critically ill patients in healthcare settings.
- Prevention of Hospital-acquired Infections: Conduct a comprehensive review of strategies to reduce hospital-acquired infections and the role of nursing in preventing them.
- Mental Health Interventions for Nurses: Focus on mental health support strategies for nursing professionals dealing with burnout and stress.
- Patient Education and Chronic Disease Management: Review how patient education impacts long-term health outcomes in chronic diseases.
- The Role of Nurses in Palliative Care: Evaluate evidence on the nursing interventions that improve the quality of life for patients receiving palliative care.
- Screening for Hypertension in Rural Populations: Review studies on how effective screening strategies are in detecting hypertension among rural populations.
- Evidence-based Interventions in Stroke Rehabilitation: Examine the interventions that have been proven to improve recovery after a stroke.
- Assessing the Impact of Nurse-led Health Interventions: Explore how nurse-led interventions improve patient outcomes in various healthcare settings.
- The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Anxiety Management: Synthesize evidence on the success of cognitive-behavioral therapy for treating anxiety in nursing settings.
- Postpartum Care Interventions: Review nursing interventions aimed at improving outcomes for new mothers during the postpartum period.
- The Role of Nurses in Reducing Health Disparities: Investigate how nurses contribute to reducing disparities in healthcare across diverse populations.
- Impact of Mindfulness on Nurse Well-being: Assess the benefits of mindfulness-based interventions for improving nurse mental health and reducing burnout.
These systematic review topics represent a broad spectrum of healthcare-related issues that are critical for nursing research. Selecting the right topic ensures that you are not only contributing to the knowledge base but also addressing real-world challenges in healthcare. Each topic should be evaluated for the available research, evidence, and potential to synthesize valuable findings for practitioners and policymakers alike.

Understanding the Structure of a Systematic Literature Review
A systematic review is a structured and methodical approach to reviewing and synthesizing existing research literature. It aims to answer a specific research question by systematically identifying, selecting, and critically analyzing published and unpublished studies. Below is an outline of the key components that make up the structure of a systematic literature review.
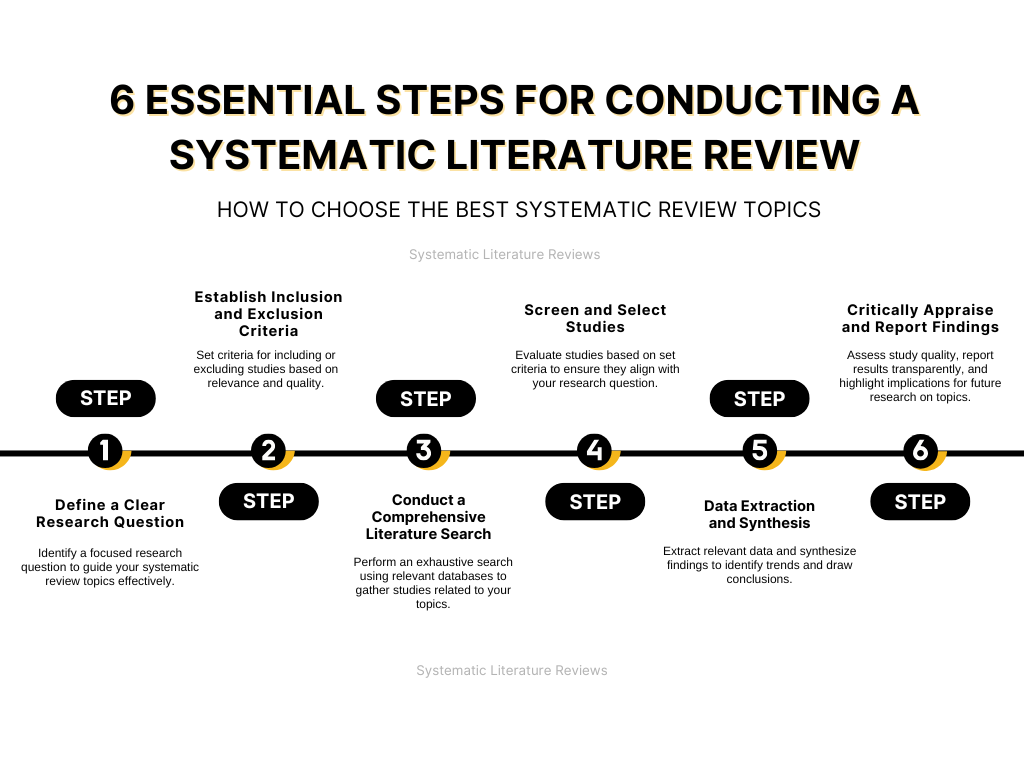
The Methodology Behind a Systematic Review: A Step-by-Step Overview
- Define a Specific Research Question: The first step is to clearly define the research question your systematic review topics will address. This ensures the review stays focused on a well-defined area of inquiry.
- Set Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Establish the inclusion criteria to determine which studies will be included in the review. This process filters out irrelevant or low-quality research.
- Literature Search: A comprehensive search strategy is used to identify both published and unpublished studies relevant to your systematic review topics. Multiple databases and sources are employed to ensure an exhaustive search.
- Data Extraction: Relevant data from each study is extracted in a standardized format to ensure that key information is consistently gathered.
- Quality Assessment: Studies are assessed for quality, ensuring that only scholarly and unbiased research is included in the review.
- Synthesize the Findings: The final step involves synthesizing the findings to provide a clear and comprehensive answer to the specific research question. This involves summarizing and interpreting the results across studies.
Identifying Literature Review Topics That Align with Your Research Question
- Focus on Existing Knowledge: A good systematic review topic is rooted in the existing knowledge base within your discipline. By understanding current research, you can select a topic that fills existing gaps in research.
- Tackle Specific Gaps: Your chosen topic should aim to identify gaps in current research or to address the question that has not been fully explored in previous studies.
- Vary the Scope: Depending on the scope of available literature, the systematic review topics you choose may need to be narrowed down to a specific area. This ensures the review is not too broad and is feasible within the timeframe.
- Future Research Considerations: Consider how the systematic review topic can inform future research. A well-chosen topic should pave the way for new research or provide directions for further exploration.
The Role of a Review Topic in Shaping the Scope of Your Literature Review
- Determine the Focus: The review topic plays a critical role in shaping the focus of your review. A narrow or specific topic will help identify gaps more easily and provide a targeted answer to the specific research question.
- Set Boundaries: The review topic helps define the boundaries of your systematic review, outlining the studies to include and excluding those that fall outside the scope. This process ensures that the review remains focused and does not stray into areas that are irrelevant to your research.
- Define the Discipline: The topic also guides the discipline of your research. For instance, selecting systematic review topics in psychology will inherently influence the type of studies included and the methodologies employed.
15 Examples of Systematic Review Topics in Psychology
- The Impact of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Anxiety Disorders: Analyze how CBT addresses anxiety by synthesizing studies from diverse settings and populations.
- Effectiveness of Interventions for ADHD in Children: Evaluate various treatment strategies for ADHD in children and adolescents, including pharmacological and behavioral interventions.
- Social Media’s Influence on Adolescent Mental Health: Review the impact of social media usage on mental health outcomes in adolescents, focusing on depression and anxiety.
- Depression Treatment Outcomes in the Elderly: Assess the effectiveness of interventions for depression in elderly populations.
- Psychological Effects of Trauma in Refugees: Synthesize studies on trauma and its psychological effects on refugee populations and identify intervention strategies.
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: Review the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for reducing stress in various populations.
- Self-Esteem and Academic Performance in College Students: Explore how self-esteem impacts academic outcomes in university students.
- Psychological Interventions for Chronic Pain: Analyze various interventions used in the management of chronic pain, focusing on psychological treatments.
- Mental Health of Healthcare Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Investigate how the pandemic affected mental health in frontline workers and potential interventions.
- Effectiveness of Psychological Counseling for PTSD: Review the impact of counseling and therapy on post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms across different groups.
- Impact of Sleep Disorders on Cognitive Function: Examine the relationship between sleep disorders and cognitive impairments, including memory and attention.
- Therapeutic Approaches for Borderline Personality Disorder: Synthesize findings on various therapeutic approaches for managing borderline personality disorder.
- Role of Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Resolution: Review literature on the role of emotional intelligence in resolving interpersonal conflicts.
- The Relationship Between Childhood Attachment and Adult Relationships: Examine how early childhood attachment influences adult romantic and interpersonal relationships.
- Psychological Factors Contributing to Obesity: Identify the psychological factors that influence eating behaviors and contribute to obesity in different age groups.
These systematic review topics in psychology represent a diverse range of questions and approaches to understanding psychological phenomena. They illustrate how systematic review topics can be applied to both theory and practice, providing valuable insights into key issues in the field.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Selecting Systematic Review Topics
Selecting a systematic review topic involves overcoming several challenges. Below are some common issues that researchers face and suggested solutions to ensure that the systematic review topics chosen are both impactful and feasible.
Overcoming the Difficulty of Narrowing Down Literature Review Topics
- Challenge: Narrowing down the literature review topic to a manageable focus can be difficult, especially when there’s a wide range of studies on a given subject.
- Solution:
- Start with a broad area of interest, but refine the focus by identifying specific gaps in current knowledge. This approach will help you narrow your search to the most relevant systematic review topics.
- Make use of a theoretical framework or model that can guide your exploration and topic selection. This can offer clarity and structure to your review process.
- Ensure the topic is answerable. The topic should be specific enough that you can comprehensively address it without overwhelming the scope of your review.
Addressing the Issue of Insufficient or Overwhelming Literature
- Challenge: Sometimes there is insufficient research on a given topic, while other times the literature is overwhelming, making it difficult to find a clear direction.
- Solution:
- If there is insufficient literature, select a topic that aligns with current knowledge but has clear gaps in research. This will allow your systematic review to contribute valuable insights to the field.
- In cases where literature is overwhelming, refine the focus by applying specific inclusion criteria. This will help you focus on the most relevant and high-quality studies.
- Use tools and databases such as University College London’s library resources, which may provide additional filtering tools to narrow down your search.
- You could also limit your research to a specific perspective or population group to make the review more manageable.
Ensuring Methodological Rigor in Your Systematic Review
- Challenge: Another difficulty is ensuring that your systematic review follows a rigorous, reproducible methodology, particularly when synthesizing data from traditional literature reviews and other sources.
- Solution:
- Use a structured, systematic approach when conducting the review. This includes predefined inclusion criteria, thorough data extraction, and clear assessment of study quality.
- Follow established guidelines, such as those in the handbook of systematic reviews, to ensure your methodology is transparent and reproducible.
- Document every step of the review process, including how studies were selected and how data was synthesized. This ensures that others can replicate your work and that the review meets methodological standards.
- Be aware of potential biases, ensuring that the critique of studies remains objective, and that the findings are statistically valid and meaningful.
Top 15 Examples of Systematic Review Topics in Medicine
- Effectiveness of Vaccines in Preventing Respiratory Diseases: Review and synthesize studies on how vaccines impact the spread and prevention of diseases like pneumonia and influenza.
- Impact of Diet on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Analyze various dietary patterns and their effects on reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Psychological Interventions for Chronic Pain Management: Review treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and their effectiveness in managing chronic pain.
- Antibiotic Resistance in Healthcare Settings: Assess the current knowledge on the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections and interventions to combat them.
- The Role of Genetics in Cancer Treatment: Explore systematic review topics that discuss genetic markers and how they influence cancer treatment outcomes.
- The Impact of Physical Exercise on Mental Health in Elderly Populations: Review studies that analyze how exercise affects mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety in older adults.
- Telemedicine’s Effectiveness in Rural Healthcare Delivery: Synthesize studies examining the benefits and limitations of telemedicine, particularly in underserved areas.
- Comparing Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Treatments for Osteoarthritis: Evaluate the clinical effectiveness of surgical and non-surgical treatments for managing osteoarthritis.
- Behavioral Interventions for Smoking Cessation: Assess the success of various behavioral approaches to helping individuals quit smoking.
- Impact of Mental Health Support on Postpartum Women: Review the effectiveness of mental health interventions on reducing postpartum depression and anxiety.
- Efficacy of Pain Relief Treatments in Cancer Patients: Synthesize data on different pain management strategies used in cancer care, focusing on their clinical effectiveness.
- Effect of Early Screening for Diabetes on Long-Term Health Outcomes: Examine how early detection and lifestyle interventions impact diabetes management.
- Nutrition’s Role in Managing Hypertension: Assess dietary interventions in reducing high blood pressure and preventing related complications.
- The Use of Stem Cell Therapy in Regenerative Medicine: Review the potential and risks of stem cell therapies in treating various diseases and injuries.
- Patient Satisfaction with Healthcare Services in Low-Income Areas: Analyze studies on healthcare quality and patient satisfaction, especially in underserved populations.
These systematic review topics in medicine illustrate the diverse and impactful areas of research that can be addressed through a rigorous and methodologically sound review process. By selecting a focused topic selection that addresses specific gaps in research, your review can contribute valuable findings to the academic community and healthcare practitioners alike.
Expert Tips and Practical Advice for Writing a Good Systematic Review
Writing a systematic review requires careful planning, precision, and attention to detail. Here are expert tips and practical advice for choosing a systematic review topic and ensuring your review is thorough, relevant, and impactful.
Leveraging Science to Choose the Right Systematic Review Topic
- Use Evidence to Guide Topic Selection: To ensure your systematic review topic is scientifically sound, start by reviewing existing literature and identifying gaps. This will help you focus on areas where research is lacking or inconclusive.
- Focus on Current Issues: Choose topics that align with current trends in your discipline. For example, emerging areas of study or research literature that need further exploration can provide a solid foundation for your systematic review topics.
- Ensure Relevance: Your review might address key issues within your field, such as understanding the effectiveness of a particular intervention or exploring new theoretical perspectives.
- Assess the Impact: Consider the potential impact of your review on practice or policy. A good systematic review topic should contribute to advancing knowledge in a practical, real-world way, making it indispensable for researchers and practitioners.
PICO Framework: A Tool for Crafting a Precise Research Question
- PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) is a widely used framework that helps in framing a focused and answerable systematic review question.
- Population: Who is the subject of your research? Is it a particular group or community, such as patients with a specific condition or a particular age group?
- Intervention: What intervention or treatment is being analyzed? This could be a medication, behavioral therapy, or any other type of intervention.
- Comparison: If applicable, compare the intervention to another treatment or a control group.
- Outcome: What results are you measuring? This could be any measurable impact like improvements in health, behavior, or quality of life.
- By using the PICO framework, you can refine your systematic review topics and ensure that your research question is specific and answerable, which makes the review process more efficient.
Finalizing Your Topic for a Systematic Review: Ensuring Focus and Feasibility
- Narrow the Scope: Once you have identified potential systematic review topics, it’s important to narrow them down to a manageable scope. A focused topic will be easier to tackle and will ensure that your research remains relevant.
- Assess Feasibility: Before finalizing your topic, assess whether sufficient literature is available for your review. Search databases like PubMed, Scopus, or those provided by institutions such as University College London, to determine whether there is enough research literature to support a thorough review.
- Set Clear Boundaries: Be clear about your inclusion and exclusion criteria. This will help you refine your systematic review topics further and ensure that your study remains focused and feasible within your timeframe.
- Feasibility in Dissertation or Research Projects: If you’re writing a dissertation, ensure that the topic you select for your systematic review is suitable for the scope of the assignment. It should be feasible in terms of time, resources, and the depth of analysis required.
Systematic Review Writing Help
Need a comprehensive systematic literature review? Let our expert team craft a meticulous review that synthesizes the latest research, ensuring your work stands out. Contact us now to get started!
Top 15 Examples of Systematic Review Topics in Social Sciences
- Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health: Review how social media use influences mental health outcomes such as depression, anxiety, and self-esteem among teenagers.
- Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions in Reducing Poverty: Assess the impact of local community programs designed to alleviate poverty in urban and rural settings.
- Influence of Parental Involvement on Children’s Academic Performance: Examine the role of parents in supporting their children’s academic success and how it affects their school outcomes.
- Mental Health Interventions for Homeless Populations: Analyze the efficacy of various mental health treatment strategies used with homeless individuals.
- Gender Inequality in the Workplace: Review studies that explore the prevalence and impact of gender inequality in corporate and academic settings.
- The Role of Education in Reducing Crime Rates: Assess the relationship between education levels and crime rates in urban communities.
- Effect of Social Support on Elderly Well-Being: Evaluate how social networks and community support affect the quality of life and mental health of elderly individuals.
- Cultural Adaptation of Psychological Interventions for Refugees: Synthesize findings on how psychological therapies are adapted for refugees from different cultural backgrounds.
- Racial Discrimination and Its Effects on Public Health: Review studies that discuss the impact of racial discrimination on health outcomes in minority populations.
- Impact of Migration on Family Dynamics: Assess how migration affects family structures, relationships, and overall well-being.
- Effectiveness of Online Learning in Higher Education: Review studies that evaluate the success and challenges of online education in universities.
- Influence of Media on Political Views in Young Adults: Examine how media consumption shapes political opinions among college-aged individuals.
- Psychological Effects of Domestic Violence on Children: Synthesize studies on the short-term and long-term psychological impact of domestic violence exposure on children.
- Social Determinants of Health in Minority Communities: Review the social factors that influence the health outcomes of minority groups, including access to care and socioeconomic status.
- Public Policy and Mental Health in Low-Income Populations: Analyze the effectiveness of public policies aimed at improving mental health services for low-income individuals.
These systematic review topics in the social sciences cover a wide range of relevant and impactful areas. Whether you’re working on a dissertation or preparing for a large-scale research project, selecting a focused and well-defined topic is crucial for success. Each example provides an opportunity to synthesize and critically analyze existing research to address important social issues and contribute valuable insights to the field.
