Blog
Understanding the Systematic Literature Review Structure | Key 5 Elements of Systematic Reviews and Literature Reviews
Key Components of the Systematic Literature Review Structure
When embarking on a systematic literature review (SLR), understanding the systematic literature review structure is crucial to ensuring a comprehensive and methodologically sound process. Below are the key components that define the structure of an SLR, which must be carefully followed for a successful review.
Systematic Review: What It Entails and Why It Matters
- A systematic literature review structure is designed to rigorously identify, assess, and synthesize existing research on a specific research question.
- The review process follows a clear and reproducible protocol to minimize bias and improve the reliability of results.
- Database searches are a critical step, ensuring that a wide range of studies is included, from peer-reviewed journals to grey literature and gray literature.
- It’s essential to understand the importance of quality assessment and to evaluate the risk of bias in each study reviewed.
- The research question is central to the systematic literature review structure, providing a focused direction for the entire process.
- A review article presents the findings of the SLR, often indicating gaps in existing research and suggesting areas for future research.
Get Expert Systematic Review Writing Help
Let Systematic Literature Reviews guide you through the entire process of writing a high-quality, transparent, and well-structured systematic review. Our experts ensure your research meets the highest standards.
Steps of a Systematic Review: Breaking Down the Structure
- Conducting a systematic review involves multiple phases, including:
- Formulating an answerable research question using the PICO framework.
- Developing search strategies that utilize database resources, such as Endnote, Zotero, or OSF, to identify relevant studies.
- Creating a PRISMA 2020-based PRISMA flow diagram to track the process and illustrate the included and excluded studies.
- Following a systematic review and meta-analysis approach to ensure all relevant data are included.
- Using a PRISMA checklist to guarantee that reporting systematic reviews adheres to recognized standards and guidelines.
How to Use a Systematic Literature Review Template for Success
- A systematic literature review template streamlines the review process, offering a structured approach to organizing included studies, excluded studies, and their findings.
- The selection process and inclusion/exclusion criteria should be based on clear, reproducible methods.
- Researchers can benefit from using tools like the university library or Cochrane reviews to access high-quality, evidence-based resources.
- The methodological rigor of the template ensures that the review is reproducible and free from biases.
- The template should also incorporate the protocol for study selection, synthesis, and peer review to maintain transparency and accountability throughout the process.
By following the systematic literature review structure, researchers can ensure that their reviews are thorough, unbiased, and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.

5 Major Chapters in a Systematic Literature Review Paper
A systematic literature review structure follows a clear framework that helps researchers organize their findings and maintain a transparent and reproducible process. Below, the five major chapters of a systematic literature review paper are outlined, highlighting key elements that should be included in each section for clarity and consistency.
Chapter 1 – Introduction: Setting the Stage for the Systematic Literature Review
- The introduction chapter is essential for laying the groundwork for the systematic literature review structure.
- Research Question: The chapter should begin by clearly stating the research question or hypothesis that the review aims to address. This provides a focused direction for the review process.
- Scope: Define the scope of the review by specifying the intervention or topic being explored. This helps narrow the focus and ensures that the systematic literature review structure remains clear.
- Background: Offer a brief background on the topic, summarizing previous reviews or research. Highlight any gaps in the current body of knowledge and justify the need for a new systematic review.
- Importance of the Review: Establish why this review matters in the broader context of the field, especially if it pertains to areas like reviews of healthcare interventions.
- Objectives: Define the objectives of the review, explaining what the study seeks to achieve and how it will contribute to the existing body of evidence.
- Keywords and Search Terms: Specify the keywords and literature search strategies used to gather relevant data, which is fundamental for ensuring reproducibility and clarity in the systematic review structure.
Chapter 2 – Methodology: Laying Out the Systematic Review Structure
- The methodology chapter of the systematic literature review structure details how the review was conducted, ensuring that the process is transparent, rigorous, and replicable.
- Research Protocol: The chapter should describe the research protocol used for the review, including the search strategy, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any methods to identify relevant studies.
- Systematic Search: Outline the systematic search process used to identify studies. This might include databases, such as PubMed, Cochrane, or others, and any assistance from a librarian to help refine search terms.
- Data Extraction: Describe the use of a data extraction form to collect relevant data from each study included. This helps ensure consistency and quality in the information gathered.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Clearly define the search and selection criteria that determined whether studies were included in your systematic review. Be transparent about any excluded studies to avoid biases in the process.
- PRISMA 2020 Statement: Reference the PRISMA 2020 guidelines or PRISMA checklist to explain how the systematic literature review structure adheres to these reporting guidelines, ensuring methodological rigor.
- Quality Assessment: Mention the tools or methods used to assess the quality systematic of studies, such as using Cochrane tools or PRISMA 2020 statement for evaluating the risk of bias.
Chapter 3 – Results: Presenting the Findings from the Systematic Literature Review
- The results chapter is where the findings of the review are presented clearly, showcasing the synthesis of the evidence in a structured manner.
- Study Overview: Provide a summary of all the studies included in your review, including their key characteristics, methods, and outcomes. You may include a PRISMA flow diagram to visually represent the number of studies included and excluded at each stage.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Data: Present both qualitative and quantitative results. Organize the findings into themes or categories based on the intervention being reviewed.
- Strength of Evidence: Discuss the strength of evidence for the outcomes, drawing on quality systematic reviews and other relevant data. Include information on whether findings were consistent across studies.
- Data Synthesis: Provide a synthesis of the findings, highlighting key trends or significant differences across studies. For reviews of healthcare interventions, this synthesis may also address the effectiveness of different interventions.
- Methods and Results Reporting: Ensure that the results are presented according to reporting guidelines (e.g., PRISMA 2020) to maintain clarity and transparency in how the findings were derived.
Chapter 4 – Discussion: Analyzing and Interpreting the Review Findings
- The discussion chapter interprets the results and places them in the context of existing research, offering insights and explaining the implications of the findings.
- Implications for Future Research: Analyze the implications for future research, suggesting areas where further investigation is needed. This might include reviewing healthcare interventions or exploring new methods of evidence collection.
- Methodological Strengths and Limitations: Critically evaluate the strengths and limitations of the systematic literature review structure, including any biases or methodological challenges encountered. Address how these limitations may impact the interpretation of the findings.
- Comparison to Previous Reviews: Compare the findings to previous reviews, noting any similarities or differences. Highlight how this systematic literature review adds new insights or clarifies existing debates.
- Interpretation of Findings: Provide an in-depth interpretation of the findings in the context of the research question. Discuss the effectiveness reviews and the practical implications for practitioners or policymakers in relevant fields.
- Recommendations for Practice: Based on the findings, offer recommendations for reviews of healthcare interventions or other areas of practice where the results can be applied.
Chapter 5 – Conclusion: Wrapping Up the Systematic Literature Review Paper
- The conclusion chapter provides a summary of the review’s main findings and their significance, offering a final assessment of the review’s contribution.
- Summary of Findings: Reiterate the key findings of the review, emphasizing their implications for the field and the research question.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Offer suggestions for future research, based on any gaps or unresolved questions that arose during the review process. This can include areas like healthcare interventions or new systematic review topics.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations in the review process, such as the methodological challenges faced or the excluded studies that may have contributed to bias.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude by highlighting the importance of the systematic literature review structure in advancing the field and encouraging further evidence-based practice.
By following the outlined chapters and adhering to the systematic literature review structure, researchers can produce high-quality, transparent, and valuable reviews that contribute meaningfully to the body of knowledge in their field.
Practical Insights for Structuring Your Systematic Literature Review
To effectively structure your systematic literature review, there are several key strategies that can guide the process. This includes leveraging the power of meta-analysis, utilizing expert resources, and following established reporting guidelines to ensure a rigorous and transparent review.
Understanding Meta-Analysis in the Context of Systematic Literature Review Structure
- Meta-analysis is an essential part of a systematic literature review structure, combining results from different studies to generate a quantitative summary.
- It involves the aggregation of data from multiple studies that meet the inclusion criteria, which allows for a clearer understanding of the research question based on empirical evidence.
- Meta-analysis helps in assessing the overall effect size of interventions or outcomes, which is crucial for understanding the strength of evidence in systematic reviews of healthcare.
Librarian’s Role in Crafting a Well-Structured Systematic Review
- A librarian’s role is vital in ensuring a systematic review structure that is both comprehensive and well-organized.
- They assist in developing an effective literature search strategy by identifying the right databases and ensuring that all relevant studies are included in the review.
- Librarians help refine search terms and make sure the search and selection process is as efficient and exhaustive as possible, improving the overall reporting of systematic reviews.
- They also assist in managing references and citations, often using tools like Endnote or Zotero, which helps maintain a systematic review manuscript that adheres to the highest standards of quality.
Using PRISMA to Strengthen the Systematic Literature Review Structure
- The PRISMA statement is a crucial tool to improve the reporting of systematic reviews by providing guidelines for clear and transparent reporting.
- The PRISMA 2020 checklist is designed to help review authors report the methods, findings, and conclusions of the systematic review, ensuring transparency and consistency in the process.
- Following the PRISMA guidelines ensures that the systematic literature review structure is rigorous, reproducible, and aligned with evidence-based best practices.
- Additionally, registering the systematic review with platforms like PROSPERO helps establish the research protocol early on, adding to the credibility and clarity of the review.
By using these insights—meta-analysis, librarian expertise, and PRISMA guidelines—you can create a well-structured and high-quality systematic literature review that adds meaningful value to the existing body of knowledge.
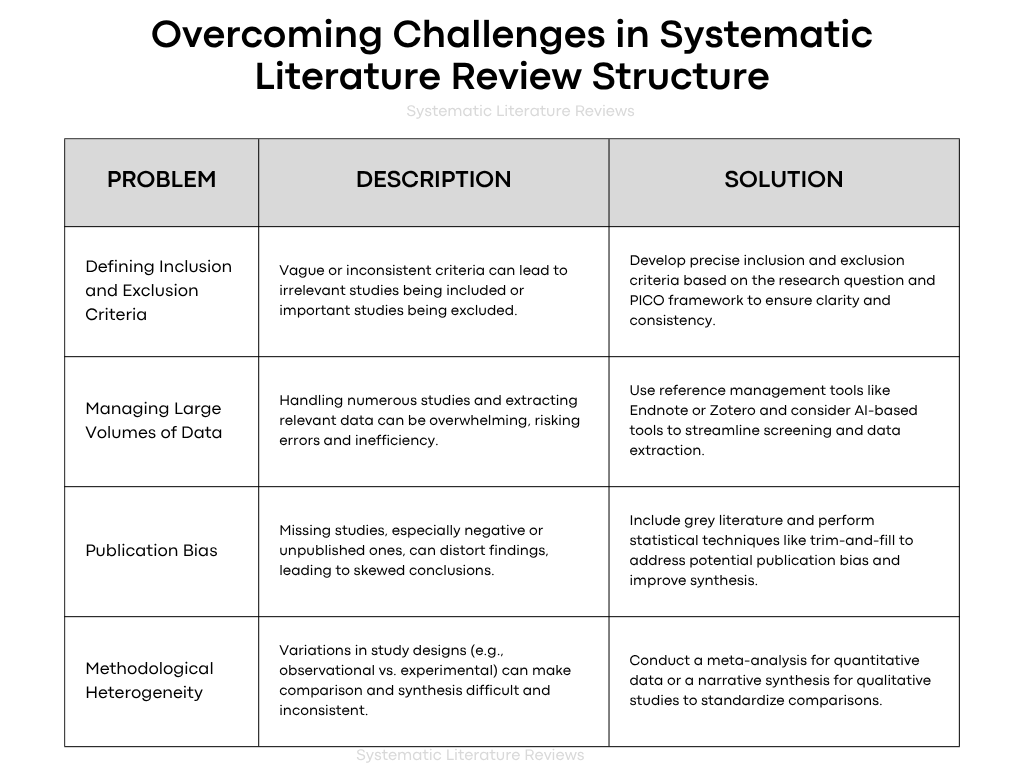
Common Pitfalls in Systematic Literature Review Structure and How to Avoid Them
While conducting a systematic literature review, it is essential to avoid common pitfalls that can compromise the integrity and quality of the review. These challenges can affect the systematic literature review structure and its findings. Below are the key issues to watch out for and how to mitigate them.
Challenges in Defining Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Systematic Reviews
- Clear criteria: One of the main challenges in the systematic literature review structure is defining appropriate inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- Criteria should be research question-based to ensure relevance and consistency across studies.
- Without well-defined criteria, the risk of bias increases, potentially leading to inconsistent data or incomplete synthesis of the evidence.
- Reviewers should collaborate early on to ensure the criteria are aligned with the objectives of the systematic review.
- To avoid this, undertake a detailed review of the types of research and ensure that only studies that meet the criteria are included, including updated systematic reviews and more recent publications.
Addressing Bias in Systematic Literature Review Structure
- Bias is one of the most significant risks in any systematic literature review structure, as it can influence the outcomes and conclusions.
- Selection bias: Arises when the inclusion and exclusion criteria are not well-defined, leading to skewed or unrepresentative data.
- Reporting bias: Can occur if studies with negative results are omitted or underreported, skewing the overall findings.
- Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews like the PRISMA statement help ensure transparency in the reporting process, addressing and reducing potential biases.
- To mitigate these issues, researchers should follow reporting guidelines like PRISMA and ensure that the systematic review structure includes all relevant data without selection bias.
The Risks of Inconsistent Data Extraction in Systematic Reviews
- Inconsistent data extraction is a critical challenge in maintaining the integrity of the systematic literature review structure.
- Data extraction forms should be standardized to avoid errors or discrepancies between studies, ensuring that all relevant details are captured accurately.
- Reviewer subjectivity can lead to discrepancies in data interpretation, affecting the consistency of results.
- Using tools like artificial intelligence can improve the accuracy and consistency of data extraction, making it easier to handle large datasets and ensure accuracy.
- To avoid inconsistent data extraction, ensure that a data extraction form is used by all review authors and that it aligns with the systematic review protocol.
By addressing these common challenges in the systematic literature review structure, you can ensure that the review process is thorough, unbiased, and reproducible, ultimately contributing valuable insights to the field.
Registering and Publishing Your Systematic Literature Review: A Librarian Guide to Finalizing Your Structure
To ensure the credibility and transparency of your systematic literature review structure, it is essential to follow specific steps in registering and publishing your review. This guide outlines the necessary steps, from registration to finalizing the structure before publication.
Registering Your Systematic Literature Review for Transparency and Credibility
- Transparency is crucial in a systematic literature review structure to maintain trust and avoid potential bias.
- Registering your systematic review with PROSPERO or a similar platform helps establish a clear research protocol from the outset. This ensures that your methodology is publicly available, offering transparency and reproducibility.
- Registration provides credibility by allowing other researchers to verify the approach and the inclusion criteria for studies, which helps prevent selective reporting.
- Registration with reputable platforms also increases the likelihood of your review being accepted and recognized by leading institutions such as the Institute for Evidence-Based or National Institutes of Health.
- Using tools like artificial intelligence during the registration process can help automate and streamline data entry, improving efficiency in the review setup.
Streamline Your Systematic Review Today
Need assistance with your systematic review? Systematic Literature Reviews offers expert writing services to help you create a clear, comprehensive, and credible review, backed by proven methodologies and expert insights.
Best Practices for Writing the Results Section of Your Systematic Literature Review
- The results section is a key component of the systematic literature review structure, where all findings are synthesized.
- Data synthesis: Provide a detailed summary of the findings from all studies included in the review. Be sure to follow clear guidelines to report the details accurately.
- Organize the results based on key themes or outcomes related to your research question. This helps readers easily navigate through your findings.
- Utilize visuals such as tables or graphs to summarize key data points, enhancing readability and accessibility of the results.
- To improve the clarity of your results, ensure the systematic literature review structure adheres to reporting guidelines like PRISMA.
- Be transparent in reporting both positive and negative findings, ensuring all data is represented fairly.
Final Steps in Completing the Systematic Literature Review Structure Before Publication
- Finalizing the structure before publishing is a critical step to ensure the integrity and completeness of the systematic literature review.
- Double-check that all sections, including the methodology, results, and discussion, are fully aligned with the research protocol and reporting guidelines.
- Ensure that all inclusion and exclusion criteria are clearly documented to avoid any confusion during the review process.
- Collaborate with reviewers to ensure consistency across the systematic literature review structure, especially in sections like data extraction and analysis.
- Before submission, ensure that your review is fully aligned with the latest reporting of systematic reviews practices. Finalize the manuscript by revising it for clarity, flow, and alignment with best practices in systematic reviews.
By following these steps, from registration to final publication, you will ensure that your systematic literature review structure is robust, credible, and transparent. This helps maintain the highest standards of academic and research excellence.
